Mathematical model of the Space
7. Nucleus of atoms
Heavy elementary
particles cooperate between themselves via fields created by them. The greatest
activity radial fields of a narrow direction have. Streams of М+ and М- in spirals of waves, cooperating
between themselves, create areas of a variable level of density and by that
influence structural elements of particles, providing their orientation, which
corresponds to a power minimum of system. Such minimum takes place at parallel
orientation of axes of rotation, an identical direction in space between
particles of vectors of intensity electric fields of gravitation of an opposite
mark and identical length of a wave of fields. Thus cooperating fields are in
one plane.
On fig. 26 the relative
positioning of structural elements of three cooperating protons, which
corresponds to a minimum of energy of system is schematically shown. Arrows show
directions of carry of a charge of Space. Vectors of intensity electric fields
coincide with a direction, shown arrows.
Fig. 26
Apparently from
figure, each proton has not balanced positive electric field. Spirals of
electromagnetic waves of these fields have an opposite direction at the next
protons. Not balanced positive fields aspire to pull together protons. In the
central area of group of protons creates underpressure of Vacuum. At
rapproachement force of interaction grows. Rapproachement occurs to education of
standing waves of М+ and
М- down to distance equal to length of a wave. On this distance of
force of rapproachement of positive fields are counterbalanced by forces of
pushing away of negative fields of electrons and
positrons.
The neutron has the
balanced fields, which become isolated against each other. The positive radial
field becomes isolated on a negative axial field. Therefore neutrons cooperate
through fields of dispersion which activity is shown only on close distances.
Thus forces of interaction of neutrons are much lower, than forces of
interaction of protons. For this reason the pulled together group of nucleons
forms stable system as two rings. On an internal ring protons are located, and
on an external ring neutrons are located. Negative radial fields of neutrons
cooperate with positive radial fields of protons and in part them compensate.
Thus intensity of a positive axial field of a neutron grows and intensity of its
negative axial field is reduced. Positive radial fields of protons get spatial
non-uniformity on an arch of a circle around of a nucleus consisting of group of
nucleons. The maximum of intensity of this field takes place near to an axis of
symmetry of an arrangement of shielding neutrons. The field of a proton gets
character of a beam of a proton.
On fig. 27А the
nucleus of atom of oxygen is shown. Arrows show an orientation of the active
fields forming beams of protons.
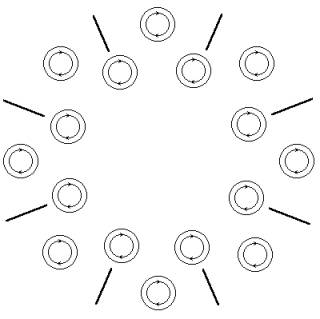
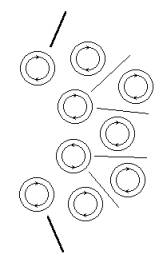
Fig. 27А Fig. 27Б
At number of neutrons
in a nucleus exceeding number of protons, the part of neutrons forms the second
ring, blocking beams of protons. The beam of a proton shielded by a neutron of
the second ring, sharply is weakened and forks on two beams which are taking
place along an axis of symmetry of negative fields of neutrons of the first and
second layer, as shown in fig. 27Б.
The beam of a proton
represents the volume of Vacuum having a power minimum in which electromagnetic
waves of not compensated positive field of a core of a proton are distributed.
On a beam of a proton carry of a charge to a direction of the central area of a
core is carried out.
The resonons, included
in structure of protons and neutrons, are located not symmetrically concerning
an axis of rotation. It creates the bias rotating weights and, as consequence,
precession of an axes of rotation. Precession axes of rotation it is caused also
by asymmetry of forces of interaction of positrons. Protons are connected by
forces of interaction in uniform system therefore precession identical period
Тp has them. Precession
coincides with a direction of rotation, therefore "top" and "bottom" of a proton
have precession, which is directed to the opposite sides. It is one more of the
reasons of elastic fluctuations of intensity of cooperating fields of a proton
and a nucleus as a whole.
Association of the big
number of nucleons in a nucleus results to that it loses symmetry to the
geometrical centre of system the local groups of nucleons having symmetry of
group are formed. As a matter of fact, it is associations of easy nucleus in one
heavy nucleus. All system is in the rotary movement subordinated to laws of
interaction of waves of separate nucleons and their groups. On this process the
indignations caused by recombination of protons and neutrons are
imposed.
In the dissociations
period of a proton, its positron can be seized by an axial field of a neutron,
which thus turns to a proton. This proton directs on an internal ring of a
nucleus, and the proton, which has lost a positron, turns to an easy neutron and
is pushed out on one of external rings.
In view of told, it is
possible to assume, that stable nucleus of atoms contain easy neutrons, and
heavy neutrons are formed at destruction of nucleus when "superfluous" positrons
and electrons are grasped by easy neutrons and protons.
If the geometry of
mutual positions of nucleons in a nucleus cyclically repeats, - the nucleus is
steady. And if the cycle does not close, the nucleus or indefinitely aspires to
steadier condition, or the cycle interrupts owing to loss of separate nucleons
or their groups. Stability of a nucleus can be broken by introduction in its
structure of superfluous nucleons. Then there is a phenomenon of an artificial
radio-activity. In the second case the natural radio-activity is observed. But
introduction in structure of a nucleus of protons or neutrons can result and in
formation of steady system of a nucleus of other element or a not radioactive
isotope. Speed of increase of changes of a wave condition of the nucleus,
resulting to its destruction, defines time of life of a nucleus. Nucleus of
atoms, are in different phases of this process. The half-life period defines
average time of destruction of 50 % of nucleus of researched
quantity.
Forwards
back
The Maximum
Knowledges (Rus)
Mathematical model
of the Space (Eng)
The Shop
