Mathematical model of the Space
6. Nucleons and hyperons
Interaction of an electron and a positron axial fields concerns to the
category of weak interactions. Between themselves axial fields two electrons or
two positrons even more poorly cooperate. At a deviation from an axial direction
during rapproachement forces of pushing away of radial fields sharply grow. But
at the moment of birth of electrons and positrons near to a peak surface of a
gravitational wave of distance between them are very small, and the probability
of rapproachement much more grows. At an identical direction of rotation of
electrons or positrons their rapproachement will take place down to interaction
of units of an opposite mark and mutual disintegration on neutrino and photons.
At an opposite direction of rotation of two electrons or two positrons mutual
disintegration does not occur owing to occurrence on the certain distance of
balance of pulses of forces for the period of the wave, working on
rapproachement and on pushing away.
On rapproachement
force of interaction of units of an opposite mark and the force caused by a
variable level of density of a charge in an axial direction operates. In the
electric field caused by underpressure in system of two electrons and
compression in system of two positrons, their photons and antiphotons direct to
the centre of rotation of system. But owing to a counter direction of rotation
their relative orbital speed more than twice above speed of rapproachement.
Therefore they periodically enter interaction in units of density of one mark,
not having time to be pulled together up to distance of a half wave. The force,
which has arisen at it of pushing away of weights of one mark, returns them in a
starting position. Thus, pulled together electrons or positrons are in an
antiphase of oscillatory movement along an axis of
rotation.
The formed structure
from two electrons has characteristics of a core of a nucleon, and the structure
from two positrons has characteristics of a core of an antinucleon. On fig. 13
the core of the nucleon, two electrons cooperating along an axis of rotation at
an opposite direction of rotation is shown.
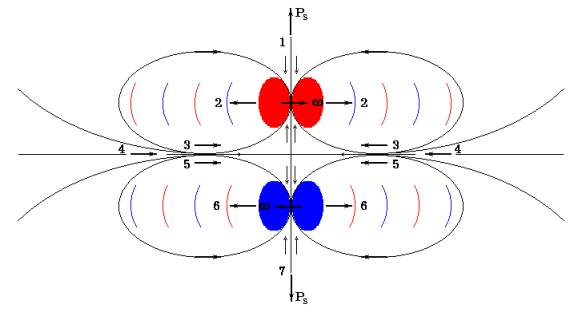
Fig. 13
Occurrence of area of
deep underpressure in the central area of a core of a nucleon has consequence
deformation of units electrons according to a configuration of an electric
field. Units will be extended in a direction of an axis of rotation, and their
radial size will be reduced. It will result in change of the moment of inertia
and increase of frequency. The length of electromagnetic waves accordingly will
decrease. Radial fields of electrons will get spiral - ellipsed the form passing
in conic axial fields. Deep underpressure of a charge in the centre of a core of
a nucleon will generate converging wave streams with frequency, which is defined
by summation of electromagnetic waves of electrons in conditions of dynamics of
mutual movings. Thus, the core of a nucleon has seven active electric
fields:
-
two
axial conic the fields of a positive mark designated in figure in figures 1 and
7,
-
two
disk fields of a negative mark, - 2 and 6,
-
two
disk fields of a positive mark, - 3 and 5,
-
one
dividing disk field of a positive mark, - 4.
All
these fields are formed by spirals of waves of an electromagnetic field,
therefore intensity of each field on distance R from a core of a
nucleon
ERe = ±1/R2 ·
EKne
(50)
Positive
and negative fields of everyone electron in structure of a core of a nucleon
become isolated against each other in the hemisphere of space, doing its active
at a great distance, is especial in a radial direction. Thickness of a disk 4 is
infinitesimal, but intensity of a field the best, as in this area, streams of
M+ and the M- of two fields 3 and 5 are
summarized in a counter direction of movement.
Intensity of magnetic
fields in a radial direction on distance R, created by the appropriate streams
of M+ and M-
НR2
= НR1 + НR3
НR6
= НR7 + НR5
НR4 →
0
(51)
The
core of a nucleon can be formed by connection of two electrons, having vectors
back PS a direction from the centre of a core of a nucleon
outside. But it also can be formed by connection of two electrons, having
vectors back PS a direction to the centre of a core of a
nucleon. Therefore the core of nucleon (Kn) can be formed in two variants: Kn-1
right and Kn-2 the left direction of rotation. Symbol Kn-1 is shown on fig. 14А,
and symbol Kn-2 is shown on fig. 14Б.

Fig. 14А Fig. 14Б
Birth Kn-1 or Kn-2 is
caused by a direction of rotation of electrons at the moment of connection. The
prevailing direction of rotation of electrons is caused by character of
polarization of photons of which they were formed. Counter streams of photons in
the field of a peak surface of a gravitational wave have mainly identical
polarization which provides their synchronization by means of a wave condition
of the Space which are taking place in one system of coordinates Space - time.
That is they are in one system of coordinates and have mutually conditioned
power communication.
The core of an
antinucleon is formed similarly by connection of two positrons. It has similar,
but an opposite mark electric and magnetic fields.
The core of a nucleon
has an active positive axial field. It can attach easy and average elementary
particles in an axial direction. We shall consider further a structure of heavy
particles. Thus we shall mean an opportunity of birth of the appropriate
antiparticles, which have a similar structure.
The core of a nucleon
can attach conic a field meson μ+ also turns thus to an easy neutron
n1. The symbol of an easy neutron is shown on fig.
15.
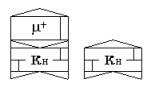
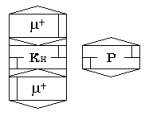
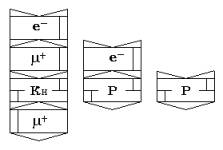
Fig. 15
Fig. 16
Fig.
17
The core of a nucleon
has fields of high frequency. Its axial fields have the big activity that is
caused by a narrow cone of an orientation of radiation. Therefore time of
existence n1 in a cloud of muons is not enough. Connection of the second
μ+ - meson transforms it into proton
Р, which
symbol is shown on fig. 16.
Axial fields of a
proton have smaller activity, than fields of a core of a nucleon. It is caused
by that frequency of μ+ - meson frequencies of a core of a
nucleon are much lower. The cone of radiation of an axial field of a proton is
much wider. γ+ - photon, which is taking place
between μ+ and Kn, rotates with intermediate
frequency and has characteristics of barion of resonon.
Connection to a proton
an axial field of electron transforms it into a heavy neutron n2 (neutron), which symbol is given on fig. 17
Consecutive connection
to a proton е-, е+, μ-, μ+ in various combinations or
connection of π - mesons and k - mesons
in various combinations creates all known scale of
hyperons. Given on fig. 18 - 25 symbols of hyperons reflect blocks of their
structure. In quality of resonons in structures of heavy elementary particles
can be γ+ and γ- photons, which in symbols are not
shown.
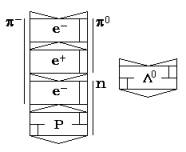
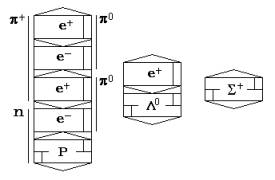
Fig. 18
Λ0 hyperon Fig.
19 Σ+
hyperon
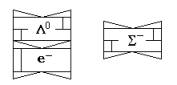
Fig. 20 Σ- hyperon
Fig. 21 Σ-1 hyperon
Σ0 hyperon, found out experimentally,
apparently, is not an independent particle, and represents
Λ0
hyperon during capture by it a γ+ photon from the side of
electron.
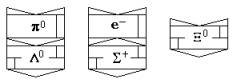
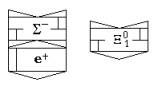
Fig.
22 Ξ0 hyperon
Fig. 23
Ξ01
hyperon
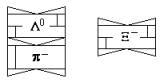
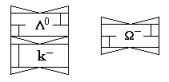
Fig.
24 Ξ- hyperon
Fig. 25
Ω- hyperon
The listed kinds of
heavy elementary particles farly from being exhaust all possible variants of
connections of electrons and photons.
Distinction of
frequencies of separate structural elements and influence of external fields
periodically results elementary particles in a dissociated condition with the
subsequent education of particles of same, or other kind. In time dissociations
can, depending on energy of external influence arise the phenomena:
-
excitation slow neutrino, taking place in immediate proximity, with
their transformation into photons,
-
transformations into photons of resonons with dispersion of energy of
rotation,
-
disintegration of electrons and positrons with transformation of
photons included in them in neutrino (fast, found out, or slow, not found
out),
-
radiation of photons and antiphotons during disintegration of
electrons and positrons or excitation of slow neutrinos.
All this
together creates a picture of various kinds of disintegration of heavy
elementary particles.
Forwards
back
The Maximum
Knowledges (Rus)
Mathematical model
of the Space (Eng)
The Shop
