Mathematical model of the Space
8. Stationary environments of electrons in
atom
Precession axes of
rotation of a proton, creates waves precessions, which are imposed on
electromagnetic waves of fields. As against the electromagnetic waves formed by
spiral streams of М+ and
М-, which have a counter direction of radial movement, waves precessions contain an agreeable direction of movement
of М+ and
М- in a radial direction. Electromagnetic waves in waves precessions
are stretched and compressed (dragged out and compressed), making wave
fluctuations with frequency precessions. The arisen wave streams become isolated
in Space, forming a field of wave precessions, which in the essence is a wave
field of symmetric gravitation.
The wave field
precessions creates sine wave changes of a zero level of density of Vacuum
Р0 and the displacement appropriate to these changes both positive,
and a negative charge. If radius precessions RP, and period
ТP, speed of movement of a point of an external surface of a core of
a nucleon in an orbit precessions
vP max = 2πRP /
ТP
(52)
and a
projection of speed to a radial direction
vP
= vP max sin ωPt = 2πRP /
ТP ·
sinωPt
(53)
Acceleration of М+ and
М- in the given direction
аP = dvP / dt = 2πRP / ТP · ωP cosωPt
or
аP =
ωP2 RP cosωPt
(54)
If to
accept, that the proton is motionless, acceleration emitted a core of a nucleon
of М+ and
М- by a spiral will be
аPKn = аKn + аP sinωKnt = 8С/TKn +
ωP2 RP cosωPt
sinωKnt
(55)
Where
TKn - the period of waves, emitted a core of a nucleon,
ωKn - angular speed of electrons in
structure of a core of a nucleon.
In absolute system of
coordinates electromagnetic waves move in the environment of a symmetric
gravitational stream of displacement of Vacuum in waves precessions. Density of Vacuum on distance R from a core of a
nucleon
PPR = 1/R
PKnsinωPtR
(56)
Where
PKn - the maximal value of density on distance R=1 from a core of a
nucleon.
Potential of the force
working on Vacuum in a radial direction
f PR = 1/R
PKnsinωPtR
(57)
Acceleration of Vacuum
in a radial direction
аPR = f PR / m PR
= 1
(58)
Length of a wave
precession on radius
owing to a constant of acceleration of displacement of
Vacuum
λPR =
аP/2 · ТP2 (2n-1)
(59)
Where n
= t / ТP
.
Distance from a core
of a nucleon up to the points of Space, which are taking place in one phase of
change Р0,
RP = аP/2 ·
ТP2 n2
(60)
Where n - integers of natural lines.
Under influence of a
positive field of a beam of a proton free electron, appeared in an operative
range of this beam, it aspires to be pulled together to a nucleus of atom.
During movement of the electron to a nucleus there is its orientation at which
the power minimum of system is provided. Therefore electron in the field of
active influence of a field of a proton has identical with it a direction of
rotation and synchronized precession axes of rotation. Thus, the steady wave
system creates a proton - electron. Between them there is a field formed by
waves extending towards precessions. At acceleration аP distance R, movings of a wave
precessions R = аP
t2 /2. Number of waves in time t
n = t / TP - φ0
(61)
Where
φ0 =
φ / 2π - a phase of a
wave in relative units.
A phase of a wave on
distance R
φR =
2πt / TP - 2πn
(62)
From
here, with the account is higher stated,
t = (2R./ аP) 0,5 = (φ/2π + n)
TP
φR =
2π((2R/ аPТP2) 0,5 – n) = 2π((R/ λ1) 0,5 – n) (63)
Where λ1 -
length of the first wave precessions.
If to accept a core of
a nucleon for the beginning of coordinates the equation of a missing wave will
look like
PKnR = 1/R PKnsin(ωPt - 2π(R/ λ1) 0,5 + 2πn)
(64)
The distance up to
point R in system of coordinates of electron, a nucleon taking place from a core
on distance Rn, is equal Re = Rn - R. The
equation moving to a core of a nucleon of a wave will look
like
PeR = -1/(Rn-R) ·
Pesin(ωPt + 2π((Rn-R)/ λ1) 0,5 - 2πn)
(65)
As
Rn = λ1n2
PeR = -1/( λ1n2 - R) ·
Pesin(ωPt + 2π((Rn-R)/ λ1) 0,5 - 2πn) (66)
Addition
of potentials of density of Vacuum of these waves up to point R
gives
PR = 1/R PKnsin(ωPt - 2π(R/ λ1) 0,5 + 2πn) - 1/(
λ1n2 - R) · Pe sin(ωPt +
2π((n2–R / λ1) 0,5 - 2πn)) =
= (1/R ·
PKn + 1/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe) sin(ωPt - 2π(R/
λ1) 0,5 + 2πn)) - 1/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe
(sin(ωPt - 2π(R/ λ1) 0,5 + 2πn) + sin(ωPt + 2π(n2–R /
λ1) 0,5 - 2πn)
= (1/R ·
PKn + 1/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe) sin(ωPt -
2π(R/λ1) 0,5 + 2πn) – 2/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe
sin(2πn - π(R/λ1) 0,5 - π(n2–R/λ1) 0,5) ·
cos(ωPt – π(R/λ1) 0,5 + π(n2–R/λ1)
0,5).
or
PR = (1/R · PKn + 1/(λ1n2 - R) · Pe) sin(ωPt –
φ1) - 2/(λ1n2 - R) · Pe sinφ2
cos(ωPt – φ3)
(67)
Where
φ1 = 2π(R/λ1) 0,5 -
2πn,
φ2 = 2πn - π(R/λ1) 0,5
- π(n2–R/λ1) 0,5,
φ3 = π(R/λ1) 0,5 -
π(n2–R/λ1) 0,5.
From here it is
possible to draw a conclusion, that in space between a proton and a electron the level of density of Vacuum is defined by
addition of potentials of two standing waves, which are having identical
frequency and taking place in an antiphase.
Potential of the first
standing wave PR1 = -2/(
λ1n2 - R) · Pe) sinφ2
cos(ωPt – φ3) has units in points R01, which
can be found from
sin(2πn - π(R/ λ1) 0,5 - π(n2–R
/ λ1) 0,5) = 0.
R01 = λ1n2
(68)
Potential of the second standing wave PR2 = (1/R ·
PKn + 1/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe)
sin(ωPt – φ1) has units in points R02, which
can be found from
1/R · PKn + 1/( λ1n2 - R) · Pe = 0
R02 = PKn / (PKn - Pe) ·
λ1n2
(69)
The electron, seized
by a positive field of a beam of a proton, moves in area of one of units of
standing waves, which arise at interaction of waves precessions axes of rotation of a proton and
electron. Thus electronic environments and subshells on distances from proton
R01 and R02 are formed. The number of subshells grows
with growth of number of electrons, standing waves participating in creation precessions.
Position of electron
in "orbit" around of a nucleus is defined by dynamic balance of all forces
working on it, from which basic:
Fe+ -
force of interaction with a positive field of a proton,
Fe- -force of interaction with a negative field of a proton,
Feg -
gravitational force of waves precessions a proton,
Fe1
and Fe2 - forces of interaction with negative electromagnetic
fields next on an environment of electrons,
Fe1g and
Fe2g - gravitational forces of waves precessions, created next on an environment by
electrons.
In a plane of radial
fields moving of an electron is limited by convexities standing waves and
negative electric fields. And in an axial direction moving of an electron is
limited precession to moving of a beam of a proton in the field of which power
minimum electron is.
The quantity of an
electrons, taking place on each environment, is limited to a balance of
interaction at which distances between next by electrons are equal both
πλ1, and
the radius of the subshells created by everyone of
electron at interaction with a proton, is equal R01 and
R02.
On fig. 28 the
relative positioning of a proton and electrons in atom and directions of the
basic forces of dynamic balance is shown.
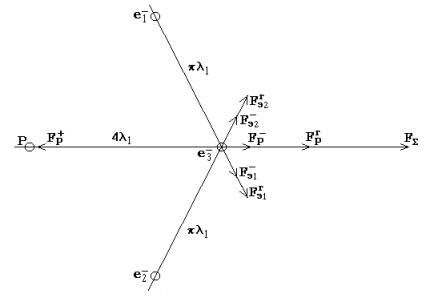
Fig. 28
Distances between by
electrons on an environment it is equal both πλ1 that is less than
distance up to the second unit of a standing wave equal 4λ1. This
position causes the intense conditions of fields. Quantity of electrons on an
environment at distances between them 4λ1
N = 2πλ1 n2 / πλ1 = 2 n2
(70)
At the greater number
of electrons in an environment, one or the several of electrons can be pulled
together up to distance λ1, appropriate to the first unit of a
standing wave. But on this distance of intensity of fields are very high.
Probability, that forces of pushing away of negative fields will overcome
oppositioning, it forces of gravitation and an attraction to a nucleus, raises.
Excessive an electron, having overcome сamber a standing wave, it is thrown out by
a wave precessions for limits of an environment.
Electron settles
down on an environment in such a manner that its backs PS it
is directed opposite a back of the appropriate part of a core of a nucleon with
which electron cooperates, and it is opposite to backs next of electrons. This
condition is carried out, when next electrons cooperate with the parts of
protons having opposite backs. At such arrangement vectors Eeg and Нg in spirals of cooperating
electromagnetic waves have an agreeable direction that provides a power minimum
of system.
The atoms having
number of neutrons, exceeding number of protons, differ that some beams of
protons are shielded by "excessive" neutrons. The weakened beams of protons,
nevertheless, are capable to keep electrons on an environment. But stability of
such interaction is lowered. Atoms easily lose these electrons and become
active.
Penetration of
everyone new of an electron on a stationary environment is connected to
overcoming a barrier, camber the standing wave formed by interaction of protons
with already taking place on environment by electrons. Overcoming of a barrier probably at presence of sufficient kinetic
energy of an electron. This energy can be is transferred to it, for
example, at collision with a photon. Thus the photon кeduces the velocity also turns in
neutrino.
Transition of electron
on more removed environment also is connected to overcoming a barrier of a
standing wave and demands starting energy. Thus transition is carried out with
speed of displacement of Vacuum in a wave of precessions, which repeatedly
exceeds speed of light. Movement of electron in area of camber the standing wave
following on a course occurs to braking in a counter stream of Vacuum. Thus the
shock wave as cones of compression of M+ and
M- in front of electron is formed. In connection with
high speed of transition of electron on a new environment, angular moving of
photons in its structure it is practically equal to zero. Therefore in front two
cones of compression are formed: a cone of M+ and a cone of the
M-, having a relative positioning appropriate to a
phase of electron at the moment of transition. At decrease of speed of electron
up to size is lower C, speeds of a wave, shock waves of M+ and
M- come off and move as the independent particle,
induced polarized a γin+
photon or a γ- photon.
Forwards
back
The Maximum
Knowledges (Rus)
Mathematical model
of the Space (Eng)
The Shop
