Mathematical model of the Space
5. Resonons and mesons
Electron and a
positron create along an axis of rotation area of variable density of a charge,
some kind of whirlpool where the photons moving aside lowered density of a
charge or antiphotons, moving aside the density of a charge raised. Thus they
aspire to be pulled together to unit of an opposite mark in structure of an
electron or a positron, get rotary movement, but can not reach this unit as it
goes with speed limit of a wave.
Frequency
characteristics of photons in structures of an electron and a positron differ
from frequency characteristics of free photons. It is consequence of
underpressure in the centre of an electron and the raised density of a charge in
the centre of a positron that results in deformation of units of photons.
Photons move to the centre, their frequency raise. The divergence of phases of
the seized photons with phases of photons in structure of an electron or a
positron results in their emission from area of interaction. The thrown out
photons γ+ or γ- some time keep rotary movement, which, as a
matter of fact, is one of kinds of polarization, and behave as the special
structural formations named as resonons.
The symbol of a
resonon and antiresonon is given on fig. 7.
![]()
Fig. 7
Capture of photons by
axial streams of M+
and the M- change conditions in the centre of an
electron or a positron owing to increase of resistance to this stream.
Accordingly, in the centre of an electron underpressure grows, and in the centre
of a positron the superfluous density of a charge grows. It changes a degree of
deformation of units of their structures. Frequency of an electron and a
positron thus is increased.
Electron, grasping two γ+ - photon, turns to rather stable particle μ-
- meson, and a positron, grasping two γ- - photon, turns in μ+ - meson. A symbol μ
- mesons it is shown on fig. 8.
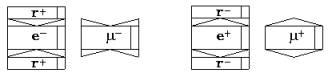
Fig. 8
Electron and a
positron at an opposite direction of rotation can not be pulled together, since
change of a direction of rotation of a stream of M+ and M-
from a positron to electron creates between them a zone of superfluous density.
At an identical direction of rotation rapproachement occurs before direct
interaction of units of an opposite mark and mutual disintegration to formation,
depending on other external conditions, a different set of photons and neutrino.
Character of
interaction will be other if it will be carried out via resonons. The stream of
a charge proceeding from a positron and working on resonon, during
rapproachement will grow. Via resonon the pulse of force will be transferred to
an electron, and rapproachement will be stopped. Thus in the centre of rotation
of an electron underpressure will increase, and in the centre of rotation of a
positron the superfluous density of a charge will increase. Their units will
come nearer to an axis of rotation even more frequency will increase. The degree
of deformation of units will increase. Frequency and degree of polarization of a
resonons will increase also. Their units also will receive additional
deformation. Differently, intensity of all internal fields of the formed new
particle will be raised, which has characteristics of a π0 - meson. A symbol of a π0 - meson it is shown on fig. 9.
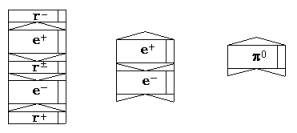
Fig. 9
π0 - meson
can grasp and throw out a resonons face fields. Electron and a positron in its
structure are synchronized via a central resonon. Periodically arising
indignations caused by small differences in frequency of photons of this system,
result in infringement of synchronism. Then synchronism can be restored, will
take place repeated synchronization. But under influence of external influences
repeated synchronization can not take place. Then there will be a disintegration
of a π0 - meson on components.
A neutrality of a π0 - meson to an environment it is provided with,
that waves of M+ and the M-, emitted the
side е+, move in
area of the lowered charge of the side е-, forming the closed wave system.
Radial fields е+ and е- are closed against each other also.
π0 - meson
can attach the second е+ via a resonon from the side е- and turn in π+ - meson. A symbol π+ - meson it is shown on fig. 10.
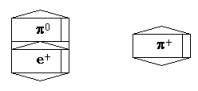
Fig. 10
π0 - meson
similarly can attach an electron on the part of a positron and will turn thus in
π– - meson. A symbol
of a π– - meson it is shown on fig. 11.
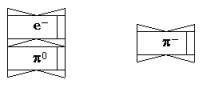
Fig. 11
Various combinations
of a π - mesons, incorporating axial fields
via of a resonons, give various kinds k – mesons, which symbol is shown on
fig. 12. Thus k0 - mesons
can arise from a
π - mesons in two variants.
Fig.12
Formation also other particles, is possible by connection by axial fields
of a π - mesons, k - mesons and μ - mesons. Connection of elementary
particles between itself changes density of Vacuum in the centres of rotation of
an electrons and positrons of which they consist. Their power characteristics
and frequency of rotation accordingly change. Disintegration of mesons can be
accompanied by destruction of structure of an electrons and positrons with mutual
disintegration as a result of which photons and neutrino are formed. Slow
neutrinos have zero power interaction with Vacuum therefore can be not always
found out at experiments. It can create visibility of discrepancy of a set of
particles of disintegration to structure of an initial particle.
Forwards back
The Maximum
Knowledges (Rus) Mathematical model of the Space (Eng) The Shop
